Materials Today Chemistry https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2025.102675
Abstract
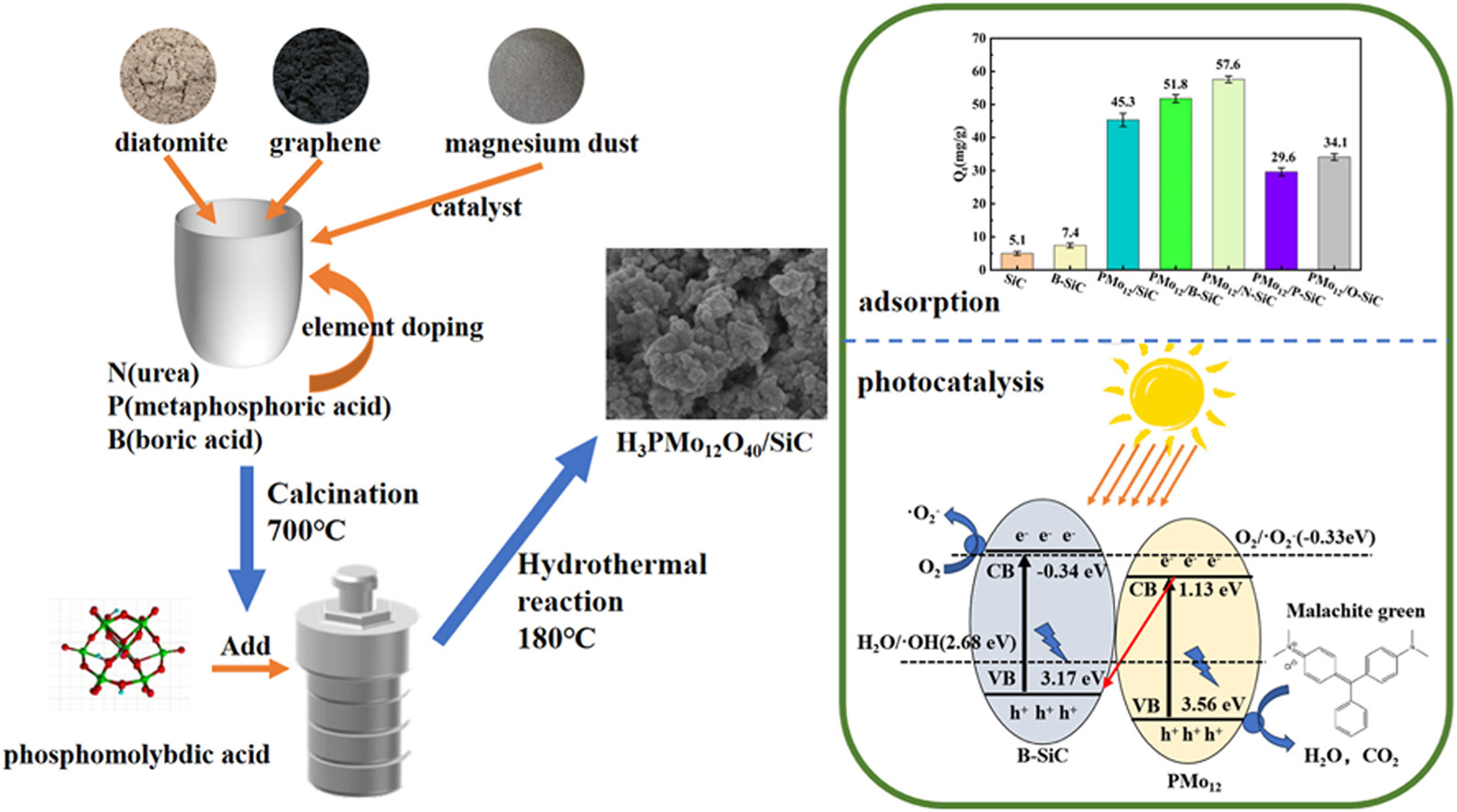
In this paper, phosphomolybdic acid (PMo12) was loaded onto nano-silicon carbide (SiC) by hydrothermal reaction to prepare a series of composites based on POM/SiC. The effects of different element doping and doping amount of SiC, the type and loading amount of POM on the photocatalytic performance of the composites were investigated. The results show that the composites have high adsorption and photocatalytic activity for organic dye malachite green (MG). Among them, pure PMo12/SiC composites have almost no photocatalytic performance for MG, but when SiC is doped with O, P, N and B elements, the adsorption and photocatalytic properties are significantly improved. Comprehensive evaluation of adsorption and photocatalytic effects, B doping has the best effect on removing pollutants. Under visible light, the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of MG by PMo12(10 %)/B–SiC composites reached 95.1 % within 120 min, and with the increase of B element doping amount, the photocatalytic efficiency gradually weakens. On the other hand, by changing the loading amount of POM in the composite material, the photocatalytic degradation efficiency is the best when the loading amount is about 5 % and 10 %. In addition, we found that the photocatalytic efficiency of PMo12/SiC was better than that of vanadium substituted phosphomolybdic acid (PMo11V, PMo10V2, and PMo9V3) composite. Finally, the charge transfer mechanism in PMo12/B–SiC composites were speculated to follow the transfer mode of Z-type heterojunction.